Egyptian Faience: The Ancient Lustrous Craft of the Nile
Step into the world of authentic ancient Egyptian faience artifacts, a vibrant ceramic art form that shimmered through the dynasties. Explore pieces from the civilization that perfected the craft of faience, capturing beauty and beliefs in glazed creations.
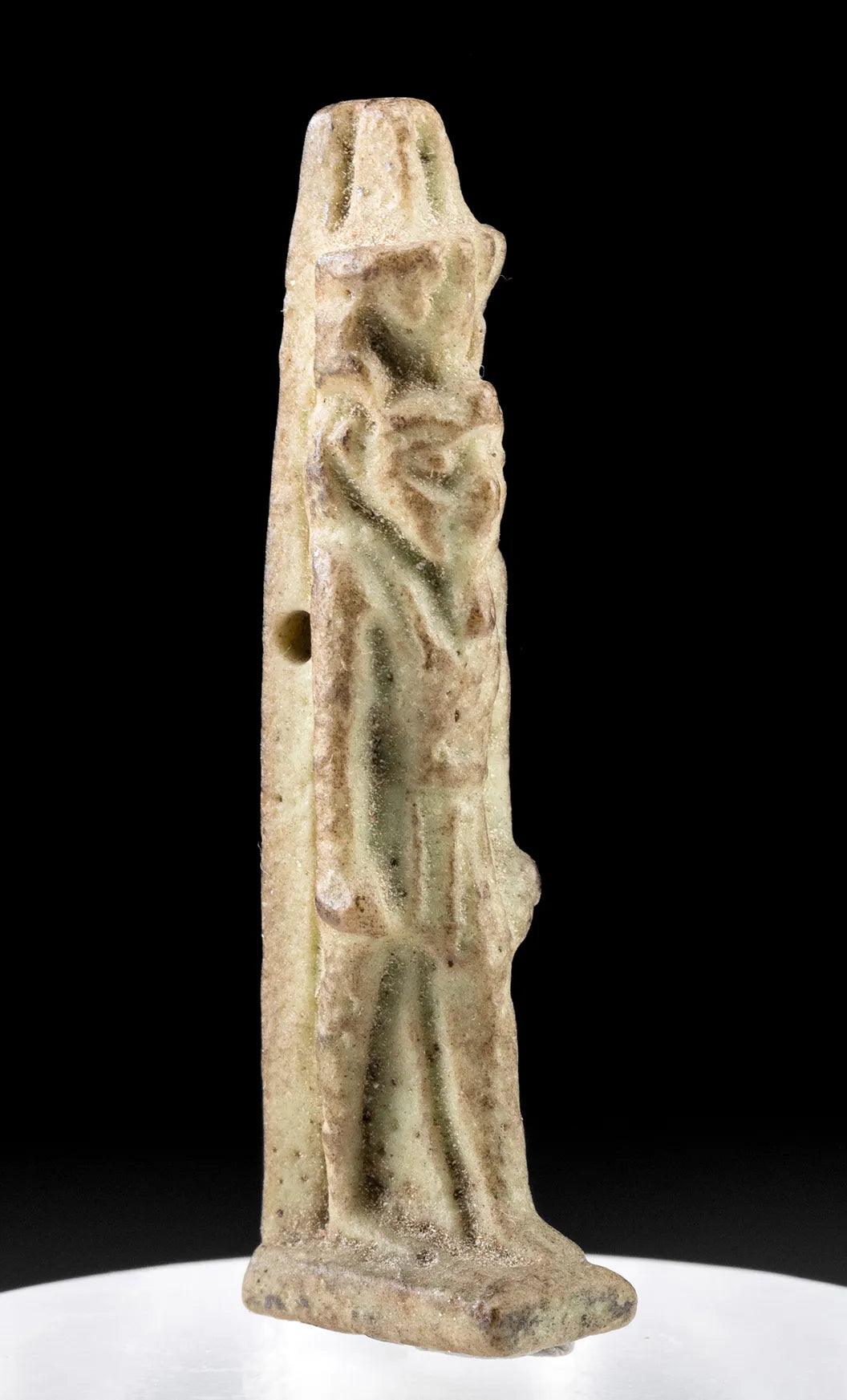
Egyptian Faience - a dazzling fusion of crushed quartz, lime, and alkaline salts, brought to life by the skilled hands of ancient Egyptian artisans. This self-glazing material, with its characteristic blue-green hue, was a symbol of rebirth, mirroring the life-giving waters of the Nile.
Importance in Ancient Times: Egyptian faience was more than just a decorative art form; it held deep spiritual and symbolic significance. The lustrous finish of faience was associated with the brilliance of the sun and the eternal cycle of life, death, and rebirth. Objects made of faience were believed to possess protective and rejuvenating qualities.
Where It Was Found: Egyptian faience artifacts have been unearthed across the length and breadth of ancient Egypt, from the tombs of pharaohs in the Valley of the Kings to the ancient workshops of Memphis and Thebes. Their presence in burial sites underscores their importance in rituals and the afterlife.
Significance in Important Objects: Egyptian faience was meticulously crafted into a myriad of objects, from amulets and jewelry to statues and tiles. The iconic blue faience hippopotamus figurines, representing the chaos-fighting deity Taweret, are a testament to the artistry and beliefs of the time. Faience shabti figures, believed to serve the deceased in the afterlife, were also common in tombs.
Cultures That Valued Egyptian Faience the Most:
- New Kingdom Egypt: The pinnacle of faience craftsmanship, with intricate designs and widespread use in tombs and temples.
- Late Period Egypt: Continued the tradition, with faience objects reflecting a blend of native and foreign influences.
- Ptolemaic Egypt: Greek rulers embraced and expanded the use of faience in various forms.
- Roman Egypt: Adopted faience for decorative and utilitarian purposes, merging Roman and Egyptian styles.
- Nubian Kingdoms: Influenced by their northern neighbors, Nubian cultures incorporated faience in their art and rituals.
Embark on a journey through our collection of genuine ancient Egyptian faience artifacts. Connect with the legacy, artistry, and spiritual depth of a civilization that turned crushed quartz into radiant masterpieces.




